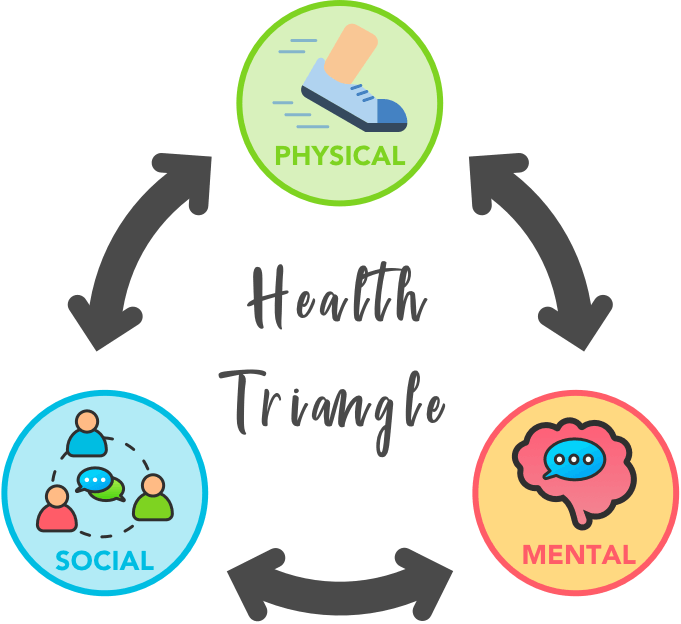
Health is a multifaceted concept, encompassing various dimensions that work together to ensure overall well-being. Among the most effective tools for understanding and achieving a balanced lifestyle is the “Health Triangle.” The Health Triangle is a simple yet comprehensive model that emphasizes three critical aspects of health: physical, mental (or emotional), and social. These interconnected dimensions provide a holistic framework for assessing and improving individual wellness.
What is the Health Triangle?
The Health Triangle, also known as the “Wellness Triangle,” is a model used to visualize the three essential components of health. Imagine an equilateral triangle, where each side represents one dimension of health: physical, mental/emotional, and social.
- Physical Health: This side focuses on the body’s overall condition and functionality.
- Mental/Emotional Health: This aspect encompasses cognitive processes, emotional stability, and psychological well-being.
- Social Health: This side deals with relationships, communication, and social interactions.
The balance among these three sides is crucial. Neglecting any one side can affect the others, leading to an imbalance that could compromise overall health. For instance, someone who prioritizes physical fitness but neglects emotional or social well-being might face challenges in maintaining long-term health.
Physical Health: The Foundation of the Body
Physical health is often the most visible and measurable aspect of the Health Triangle. It refers to how well your body functions, encompassing various factors such as nutrition, exercise, sleep, and the absence of disease.

Key Components of Physical Health
- Nutrition: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins is essential for energy and cellular repair.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity improves cardiovascular health, strengthens muscles, and enhances flexibility. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate exercise per week.
- Sleep: Quality sleep is critical for recovery, brain function, and overall energy. Adults should strive for 7-9 hours per night.
- Preventative Care: Regular medical check-ups, vaccinations, and screenings can prevent illness and detect issues early.
Tips for Enhancing Physical Health
- Stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day.
- Incorporate both aerobic exercises (like walking or swimming) and strength training into your routine.
- Avoid harmful habits such as smoking, excessive alcohol consumption, or a sedentary lifestyle.
- Manage stress effectively, as chronic stress can lead to physical health issues like high blood pressure.
By prioritizing physical health, you lay the groundwork for a strong and resilient body that supports other dimensions of wellness.
Mental/Emotional Health: The Heart of Well-Being
Mental and emotional health is often overlooked, yet it is integral to a balanced Health Triangle. This dimension encompasses how individuals process thoughts, manage emotions, and cope with challenges. Emotional resilience and a positive mindset contribute significantly to overall well-being.
Key Components of Mental/Emotional Health
- Emotional Regulation: The ability to manage and express emotions appropriately.
- Stress Management: Techniques such as mindfulness, meditation, or deep-breathing exercises can help reduce stress.
- Mental Clarity: Maintaining focus, making decisions, and problem-solving effectively.
- Self-Esteem: A positive self-image fosters confidence and reduces vulnerability to mental health issues.
Signs of Good Mental/Emotional Health
- Feeling content and optimistic.
- Having the capacity to manage stress effectively.
- Maintaining healthy coping mechanisms during challenging situations.
Tips for Improving Mental/Emotional Health
- Practice Gratitude: Reflect on things you are thankful for to foster a positive outlook.
- Seek Support: Talk to friends, family, or a mental health professional if you’re struggling.
- Set Realistic Goals: Break tasks into smaller steps to avoid feeling overwhelmed.
- Engage in Hobbies: Activities you enjoy can reduce stress and promote mental well-being.
Mental and emotional health is deeply interconnected with the other sides of the Health Triangle. For instance, regular physical activity releases endorphins, which can elevate mood, while positive social interactions reduce feelings of loneliness.
Social Health: The Power of Connection
Social health emphasizes the importance of relationships, communication, and a sense of belonging. Humans are inherently social beings, and the quality of our interactions with others significantly impacts our overall health.
Key Components of Social Health
- Healthy Relationships: These include family, friendships, and romantic partnerships that provide support and encouragement.
- Effective Communication: The ability to express yourself and listen actively.
- Community Engagement: Participating in group activities, volunteering, or other community-driven initiatives. Newfashiontech.co.uk
Benefits of Good Social Health
- Lower levels of stress and anxiety.
- Increased sense of belonging and purpose.
- Better coping mechanisms during challenging times.
Tips for Enhancing Social Health
- Build Strong Relationships: Invest time in nurturing relationships with people who uplift and support you.
- Join Social Groups: Participate in clubs, sports, or community events to meet new people.
- Resolve Conflicts: Address issues in relationships calmly and constructively.
- Limit Toxic Relationships: Distance yourself from individuals who drain your energy or create negativity.
Maintaining social health requires effort and intentionality, but the rewards are invaluable. A robust support network can provide comfort and guidance, especially during tough times.
The Interconnection of the Health Triangle
While each side of the Health Triangle is unique, they are deeply interconnected. Neglecting one aspect can create a domino effect that disrupts overall well-being. For example:
- Poor physical health can lead to mental health challenges like anxiety or depression.
- Emotional stress can strain social relationships.
- A lack of social support can make it harder to stay motivated for physical self-care.
Conversely, strengthening one side of the triangle often benefits the others. Regular exercise, for instance, improves physical health, boosts mood, and provides opportunities for social engagement (like joining a fitness class).
Balancing the Health Triangle
Balancing the Health Triangle is a lifelong journey. It requires self-awareness, intentionality, and a commitment to holistic well-being. Here are some practical strategies:
- Conduct Regular Self-Assessments: Periodically evaluate how you’re doing in each dimension. Identify areas that need more attention and set realistic goals.
- Adopt a Growth Mindset: Understand that balance is not static. Life circumstances change, and your approach to health should adapt accordingly.
- Prioritize Self-Care: Allocate time for activities that nourish your physical, mental, and social health.
- Seek Professional Help: Don’t hesitate to consult healthcare providers, therapists, or counselors when needed.
Conclusion
The Health Triangle is a powerful reminder that true wellness goes beyond physical fitness. It requires nurturing your mind, emotions, and relationships. By striving for balance among the three sides—physical, mental/emotional, and social health—you can achieve a more fulfilling and resilient life.
Remember, the Health Triangle is not just a concept but a practical guide. Use it to identify imbalances in your life and take steps to create harmony across all dimensions of health. In doing so, you’ll unlock the full potential of your well-being and lead a healthier, happier life.